How to Quickly Get Your Site to the Top of Google [SEO Made Easy]
Before we dive into mastering Search Engine Optimization, it's crucial to acknowledge the dynamic nature of the emerging strategies shaping the landscape.
We're in an era where understanding the intent behind search queries— semantic search—is more vital than focusing solely on specific keywords. Rather than flooding the first page results with websites containing keywords, you're provided a collection of relevant information.
"How can I get to the top of the Google search results fast, and stay there?!"
This seems to be the question every business owner or marketing director wants to know the answer to.
Yes, there are hundreds, if not thousands, of ranking signals that Google takes into consideration, along with constant updates to each algorithm, but the core elements of successful search engine optimization will almost always stay the same.
We get it though...
Search Engine Optimization is a daunting and somewhat mysterious topic for a lot of marketers. And although organizations are aware of how powerful SEO can be, most in-house marketing teams simply don't know where to begin.
That's why today our team at Trailblaze Marketing is going to walk you through exactly how to get your business to the top of Google, and look like a marketing hero doing it.
Here's exactly what we'll cover:
-
Your Foundation: Learn how to quickly get your website in shape
- Ranking Factors: See what matters most
- On-page Basics: Structure each page this way and you're golden!
- Content: How do you create & leverage content properly?
- Link Building: Building a sustainable link acquisition strategy for rankings
(Quick note: SEO has a lot of moving parts. If you find yourself struggling to figure out how each component works together, you might benefit from our website & SEO audit.)
Your Foundation
The first position in Google's search results has a 31% click-through-rate.
Yep, you read that right. And the first step in getting there is making sure your website is clear of any obvious issues.
I'm not talking about about a super in-depth technical audit, but rather a check for any server or security issues, crawl and/or index restrictions, overall indexation, crawlability, crawl rate, site speed, penalties, HTML improvements, etc.
Essentially, we want your website to have a clean and solid foundation to build off of as we progress further into on-page SEO, link building, and more.
Here's exactly what to do:
1. Head over to Google Search Console:
This is a free, yet super powerful tool for SEO that every webmaster and digital marketer should have access to.
Your Search Console is comprised of 4 major sections:
- Crawl: Here you'll see your site exactly as Google sees it. This section mainly consists of URL and site errors (DNS errors, 404 codes, server errors). Through crawl, you also have access to the crawl stats report. This data tells you how often and when Google is crawling your website. These charts should have consistent fluctuations with minimal change.
- Index: In the index section of Search Console you'll see information about the URLs that Google is actively including in their index. You want to make sure the pages being indexed by Google matches the pages receiving traffic in Google Analytics. If this is not the case, you're likely experience index bloat, an issue where pages are indexed when they shouldn't be (think category tags, archives, secure and non-secure versions of your site, etc.).
- Traffic: This is an important part of your Google Search Console. Here you'll see web traffic analytics such as impressions, clicks, CTR, and position, broken down by page, device, date, and more. This section also gives you access to all links pointing to your site, internally and externally, in addition to penalties and the mobile usability of your site.
- Appearance: Lastly we have the appearance section. Here you'll see any issues regarding how your organic listings appear in the SERPs. This includes information regarding the schema mark-up on your site (more on that later), HTML improvements proposed by Google (duplicate titles, missing descriptions, etc.), a review of your accelerated mobile pages (AMPs) and more.
In this section, we're going to mainly talk about crawl and index (and how to quickly get your site into shape).
First, check out what Google has to say under the Current Status. You should be looking for any response codes that aren't labeled as 200. Make sure everything is good with your server, redirect any 404's, and address any redirect chains (redirecting to a redirect).
Here's a brief overview of the HTTP status codes you may encounter:
- 100 Codes (Information): The server has received and understood the request, but has not yet approved it
- 200 Codes (Success): The server has received, understood and approved the request
- 300 Codes (Redirection): These codes indicate that the client must take additional action to complete the request; common 300 codes include 301 redirects (permanently redirecting one page to another) and 302 redirects (temporarily redirecting one page to another)
- 400 Codes (Errors): These codes indicate an error caused by the client; these include bad requests (400), unauthorized access (401), payment required (402), forbidden requests (403), and of course requests not found (404).
Now, head over to where it says Google Index.
Here you'll see the number of pages Google is currently including in it's index. Cross reference this number with the pages included in your site map (more on that soon) and also be sure to check out blocked resources.
Here you'll see exactly what your robots.txt (the file that tells Google how to crawl your site) is communicating to Google. Ensure the pages being blocked should actually be blocked.
Next, head down to crawl. Make sure there are no known errors. You'll also want to confirm you've submitted an XML sitemap (this tells Google what pages it should consider when indexing).
The relationship between your robots.txt file and XML sitemap is very important. Make sure one is not contradicting the other.
Remember:
These two things are absolutely imperative in making sure your site can be crawled as efficiently as possible, and you're not wasting your precious crawl budget on low-quality, irrelevant pages (the amount of pages Google will crawl on average; more trusted and authoritative sites are crawled more).
2. Check out your site speed!
On average, 40% of your website visitors will bounce if it takes longer than 3 seconds to load. That's scary, and a good reason for you to optimize your sites speed.
Use Google's PageSpeed Insights tool first. Although it may not be the industry preferred tool, it will give you a solid estimate of your page speed, in addition to a starting point.
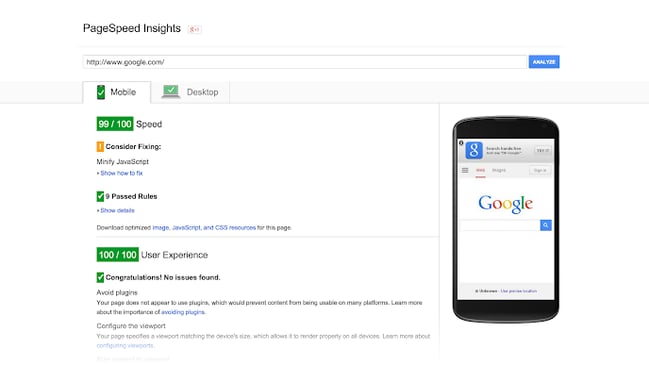
Some things you should look for immediately:
- Browser caching
- Image optimization
- GZIP compression
- JavaScript/CSS issues
- Redirect problems
- Server related issues
Next, we recommend cross-referencing all of this in a tool like GTmetrix.
Here you'll see the exact improvements you should make, in addition to a waterfall illustrating how your page is currently utilizing system resources.
Your site speed is incredibly important nowadays so make sure to get it right!
If you're a WordPress user here are a few plugins that will save you a lot of time by addressing most of the issues above:
- WP Fastest Cache: render your page quicker
- WP Super Minify: compress JavaScript and CSS files
- WP Smush It: quickly reduce image size
- BJ Lazy Load: delays page loading until a user scrolls down
IMPORTANT: Every plugin will interact with your website theme differently. Make sure you back-up your site and check for any design or functionality issues after each plugin is activated.
Check out the Moz learning center here for more information on improving your site speed.
3. Internal Linking
Looking to quickly boost a page up in Google search? Look no further.
Internal linking is suuuper important for your sites navigation, information hierarchy, crawlability and the passing of your link equity (the influence or power a page has).
Links are considered the highway of the Internet.
When you link from one page to another, you're essentially giving it a vote of confidence (which Google notices). In addition, your making Google's job easier (which they also notice) by creating a structure that is easily crawlable for them.
So how do you leverage internal linking to get to the top of Google?
You internally link from authoritative pages (high link equity) with relevant anchor text (text describing the link) to pages you'd like to move up.
This is why creating a site architecture with link silos is so important. Regardless of where on your site an inbound link comes in, every page in that silo will be affected.
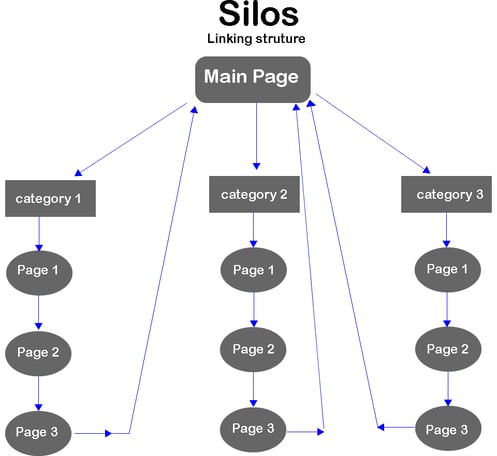
The trick to effective internal linking is to be as natural as possible. The more contextually relevant, the better.
Check out this article on best practices for internal linking.
4. Engagement
We can bring all the traffic in the world to your site, but if its not designed to convert or at least hold a prospects attention, your SEO efforts will be worthless.
In addition, Google's algorithms' are shifting and putting more weight on user experience signals like bounce rate, pages per session, time on site and more.
The solution?
Design pages that are valuable and shareable. This may sound overly simplistic, but it's not. As long as every page has a purpose and provides real value, Google will eventually take notice simply by the engagement, amplification, links, and more.
Here are some quick ways to increase the engagement on your pages:
- Use high-quality images
- Improve your readability (bold text, spacing, bullet points)
- Incorporate video!!!
- Use content upgrades
- Leverage contextually relevant CTA's
Above all, images and video are one of the quickest ways to increase your levels of engagement. Be smart about your usage of media and Google will take notice.
5. Architecture
Mobile, mobile, mobile.
If you've read anything related to digital marketing, you've probably heard of mobile responsiveness and its importance.

The thing is...
It's not just important anymore... it's a necessity!
See, Google recently rolled out their mobile-first index. What's that mean for SEO?
They're now ONLY looking at the mobile version of your website! So the next question is... how do you optimize for mobile?
Mobile users behave a lot differently than desktop users, and require a much different experience as a result.
For an in-depth look at how you can optimize your site for mobile, check out this definitive guide by Brian Dean.
When we think about website architecture a few other important things here are your information hierarchy and URL structure.
Your hierarchy is simply the organization of your website. This is important for crawlability, user experience, and more. There's nothing worse than having to click through 4 pages to get to the single page you need.
Organize your site in a way that is logical, helpful, and simple. Your users will thank you.
The architecture of your site will affect your URL structure too. Believe it or not, shorter URLs rank better than longer ones.
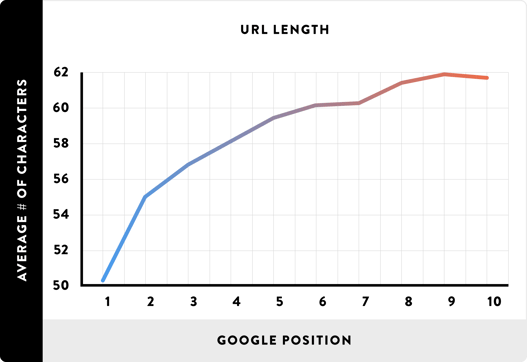
Your site's architecture is a monster of a topic that can't possibly be covered in full by this one piece of content. For a great resource, check out this post at Search Engine Land.
Also, performing a comprehensive website and SEO audit is sometimes needed to fully uncover the issues holding your site back.
Ranking Factors
Before we get too into the weeds, let's take a step back to remember what variables we're trying to change. It helps to refer back to this list from time to time too, as it can be a quick source of motivation.
Cyrus Sheppard put together a comprehensive list of 100+ SEO success factors ranked by importance.
This post is, by far, the most relevant piece of content out there on this topic, and it's easy for just about anyone to comprehend.
Here's a preview of the top success factors:
1. Content that targets user search queries
2. Crawlable + accessible to search engines
3. Quality and quantity of links
4. Satisfies user intent
5. Uniqueness of content
On-page Basics
A page with proper on-page SEO can work wonders for getting to the top of Google. And for those of you lucky enough to already have a website with high domain authority, your on-page should be flawless.
This is because your pre-existing authority means you'll have a much easier time trying to rank for a keywords.
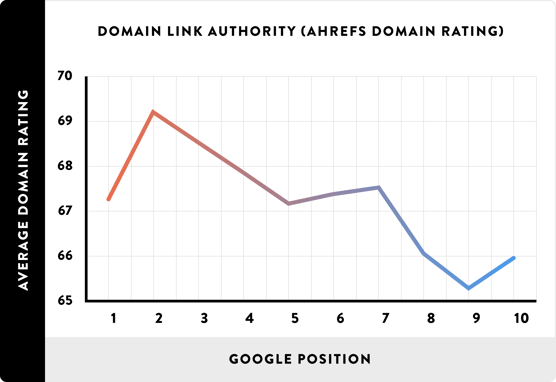
(Clear correlation between domain authority and rank, according to Backlinko)
In any case, here's exactly what you need to pay attention to:
- Crawler Access: OK, before you get into your meta data or page headings, can Google even crawl your f*ck*ng page?! (Sorry... bad experience here). But seriously... Check to make sure your URLs are static and NOT dynamic (they stay the same and don't change), 301 redirect any outdated content (or 404s) to your page, make sure the page content is unique to THAT URL (all duplicates canonicalize to it), ensure your content loads directly in the page HTML (not iFrames, AJAX, etc.), double check your Robots.txt to verify there are no restrictions on crawler access, and make sure the page URL is included in your site map.
- Title Tag: When I write title tags, I often try to think what would sell this click? But not in a phony, used car salesman way, because remember: we don't want ALL the traffic, we want the RIGHT traffic! In fact, your title should qualify the prospect for your page. Include words that describe whether your page is informational, purchase based, includes a download, etc. Then, make sure to include modifiers and power words like best, 2018, free, powerful, proven, easy, etc. (Important: target only ONE keyword per title, keyword cannibalism is a mistake I see ALL the time).
- Meta Description: Your meta description is an even better opportunity to sell the click. Although this is not a direct ranking factor, you have up to 320 characters to describe the page and qualify your prospects. Make sure your primary and secondary keywords are included (they'll be bolded) and you've adequately summarized the content on your page.
- Heading Tags: Generally, the header 1 on your page should be the same as your title (although some SEO's suggest a primary variation), regardless, include your primary keyword there and you're good. Next, optimize your header 2 tags to reflect the secondary keywords (or primary variation) your page is targeting. You can have multiple h2's but be sure to only use one h1. Missing header tags (especially header 1) is an on-page mistake I see ALL the time.
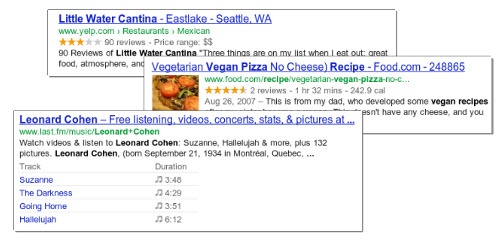
- Images: A page consistently merely of text is BORING. Images also increase time on site and decrease bounce rates. Visual representations of data, like infographics, are an excellent way to communicate information, get back-links, and send positive user interaction signals to Google. For any images, be sure to include ALT text and a relevant file name.
- Video: Want to increase transparency, authority, AND engagement? Invest in short videos showcasing your products, services, or brand. Once again, videos will decrease bounce rates drastically. The benefits of video in 2018 are countless.
- LSI Keywords: Contrary to popular belief, LSI keywords are not synonyms. They are words related to your primary or secondary keywords. An LSI keyword for the word football might be Ohio State or New England Patriots. Incorporating these words on your pages gives Google more context to work with when trying to understand your page. We want Google to understand our page so they can rank us accordingly! Head over to LSI Graph, pop your keyword in, then take the results and sprinkle them within your content (where it makes sense).
- Internal & External Links: Linking, whether it's linking within your site or outside of your site, it's absolutely necessary. External links to related, authoritative pages are a relevancy signal to Google, and help the search engine understand what your content is about. In addition, internal links spread link equity, which for product and service pages that don't receive many links, is huge! Try to use one internal and external link for every 500 words that you write.
- Schema Mark-Up: Schema Mark-up, or structured data, tells a search engine like Google what your data MEANS, not just what it says. In regards to getting to the top of Google, this is huge. There are hundreds of types of data mark-up, including: articles, local businesses, book reviews, movies, events, and more. Learn more about implementing schema mark-up here.
- Social Sharing: Social sharing buttons are a must have on every page. A study found that prominent social sharing buttons increased social shares by 700% (who would of thought?). In addition to the instant amplification your content will receive, social signals are something Google very much pays attention to.
- Content: Is your content uniquely valuable? Is it immediately obvious that the quality is head and shoulders above your competition? Would 80%+ of your visitors describe your content as useful, high-quality, and unique? Would a prospect searching for your target keyword feel compelled to go back and choose a different result? If you can't provide the right answer to these questions, you need to go back to the drawing board.
Check out this case study to see exactly how we leveraged on-page SEO for insane organic growth.
Content
When it comes to your SEO strategy, content really is everything (notice how I didn't say king?).
In fact, according to Content Marketing Institute, content development costs 62% less than outbound marketing tactics AND generates 3x as many leads.
But remember: Quality is far more important than quantity. One long-form, super in-depth guide with 2000+ words carries a lot more value than 10 vague, 300-word posts that barely scrape the surface.
Comprehensive content like guides often rank for high purchase intent keywords too. Speaking of intent, you need to pay close attention to WHY a prospect has landed on your site. This is, by far, the most important part of developing amazing content.
Although your content creation will mainly be guided by your keyword research, you still need to ask yourself the following questions:
- What problem is this content addressing?
- What is the intent of the users who will land on my page?
- Does my content fulfill their needs?
- What would make someone link to this content?
- Why would someone amplify or share this content?
Addressing these core questions early on will ensure that your content is shared and linked to. Put your empathy cap on and start thinking like your prospect.
Check out the Free Beginners Guide to Content Marketing from Moz.
Link Building
Building links is considered by many to be the most difficult part of search engine optimization. If you're new to SEO you may be wondering...
What's all this talk about link building about? What's the point?
Links are used by search engines to crawl the web. When crawling, Google will discover new web pages (that they may or may not include in their index) and then decide how well a particular page should rank (largely based on the number of links they just discovered pointing to that page).
A little history...
Links are what allowed Google to dominate as a search engine in the late 1990's. This led to the first algorithm (created by Google co-founder Larry Page) called PageRank. It measured the quality of a page based on the quantity of links pointing to it, and it worked extremely well. That is, until SEOs discovered how to manipulate it.
Fast forward to SEO in 2018, and links are still considered one of the most important ranking factors (if not the most important). The difference now?
Google looks at much more than just the quantity of links a page or website as a whole receives.
The velocity, diversity, anchor text, relevancy, page position, and of course quality of the links you're receiving all play a HUGE role now.
So how do you build a link acquisition strategy that checks off all of these boxes?
There are many tactics. The appropriate one for your organization largely depends on the resources you have available (content, budget, time, etc.) and the industry you're in.
A few common, and mostly successful link building tactics include:
- Content-based link building: Building links with content is exactly what it sounds like. Develop an amazing resource (a long-form guide, infographic, video, white paper, image gallery, etc.) then perform outreach and promotion to place your links in contextually relevant areas across the web.
- Guest posting: Guest posting is a link building tactic that involves approaching other websites and pitching a piece of content in an attempt to have your post shared on their blog. Although it's still very effective, guest blogging is one of the most abused tactics in the SEO world today. Approach with caution as Google has gotten very good at discovering various types of link manipulation.
- Link reclamation: This tactic involves finding mentions of your product, service, brand, employees, etc. that do not include a link. The process involves reaching out with a pitch as to why the content should include a link.
- Competitive link sniping: Does your competitor have a link profile you're envy of? Well, why reinvent the wheel? Steal some of theirs! Plug your competitors URL into an SEO tool like SEMRush, OpenExplorer, or Ahref's. Next find the sites linking to your competitor and see if these same sites would link to you.
- Round-ups: Round-ups typically involve gathering experts around a specific topic or building a top list of links, blogs, products, etc. The hope is, by including those mentioned, they'll feel inclined to share and amplify the content, resulting in links. One brand that executes this tactic particular well is Databox.
- Broken link building: Exactly as it sounds, broken link building involves scouring the web for links that are no longer working. The SEO then reaches out with a piece of content similar to the one found on the broken link with a pitch for why it should be replaced with the new link. Broken link building can also be performed on ones own site, as websites with thousands of pages can easily accrue links that no longer work. This is a great opportunity for a 301 redirect to pass that link equity to a page that works.
- Ego bait: Ego bait is content-based link building, with others mentioned in the content. The hope is that, by playing on the egos of those mentioned in the content, they'll be more inclined to share and link to it. A common type of ego bait is a list based post featuring companies, influencers, blogs, etc.
- Skyscraper Articles: The skyscraper link building technique is one of the most effective, if I do say so myself. This tactic involves finding a piece of content in your industry that already has numerous linking root domains, creating a BETTER piece of content, and reaching out to the sites that linked to the original content and convincing them to link to you.
For more help with link building check out this helpful resource over at Moz.
Our team hopes you found value in our beginners guide to ranking on the top of Google.
Our goal was to walk you through each aspect of SEO, in hopes of breaking this topic down into layman's terms.
Now that you have a solid overview of what SEO looks like, it's time to start pumping out content, building links, and learning as you go.
Effective SEO is consistent and slow.
That's right... it's slow...and it takes A LOT of patience.
Editor's Note: This blog post was originally posted in January 2018, but has since been updated for accuracy.







